Delaware Statutory Trusts
Delaware Statutory Trusts (DSTs) allow investors to participate in real estate ownership without the day-to-day management tasks. As legal entities, DSTs let multiple investors buy fractional interests in high-quality, professionally managed properties, offering a passive way to invest in large-scale real estate.
DSTs: The Go-To Alternative for 1031 Investors
For years, Tenant in Common (TIC) ownership was the go-to structure for passive 1031 investments. However, over the last 25 years, Delaware Statutory Trusts (DSTs) have gained popularity among sponsors and investors. DSTs provide centralized management and streamlined decision-making, making them a top choice for passive real estate investments.
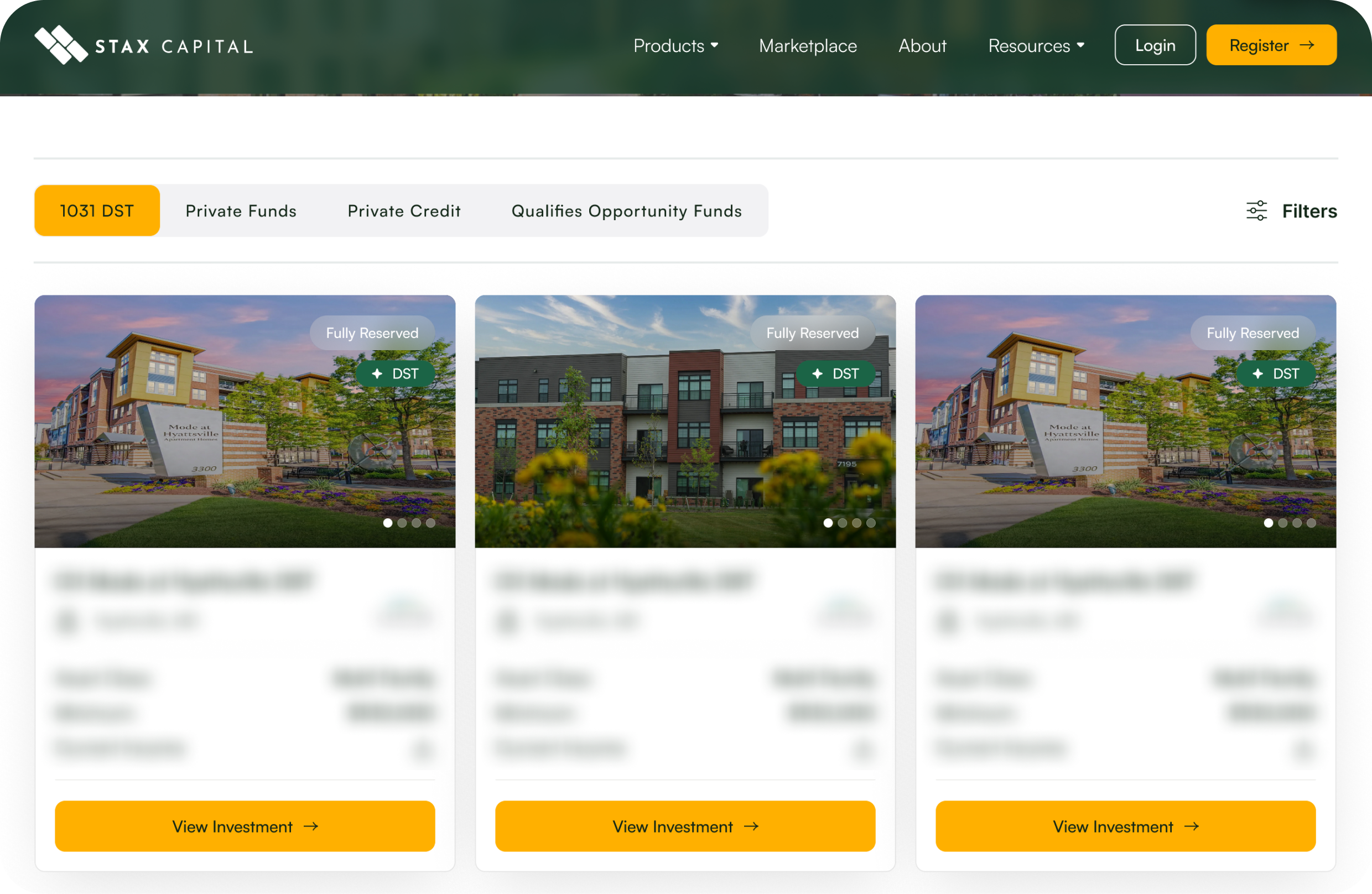
New DST Properties
Access top-tier real estate investments through our newly listed DST properties, built for 1031 exchange and portfolio diversification.
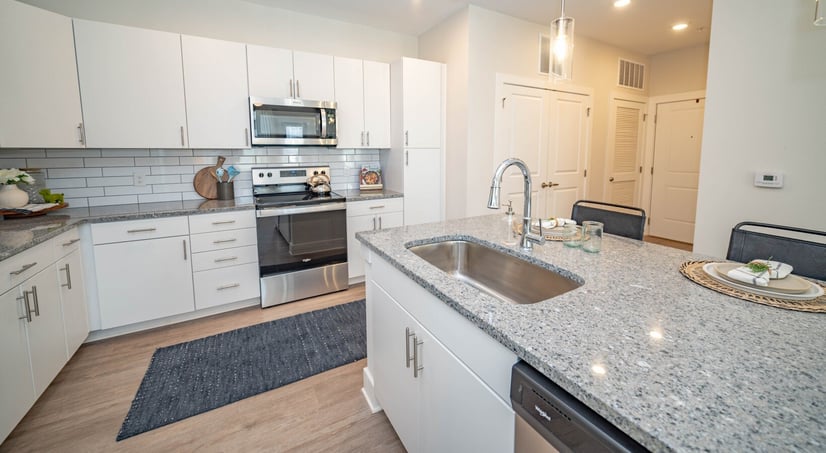







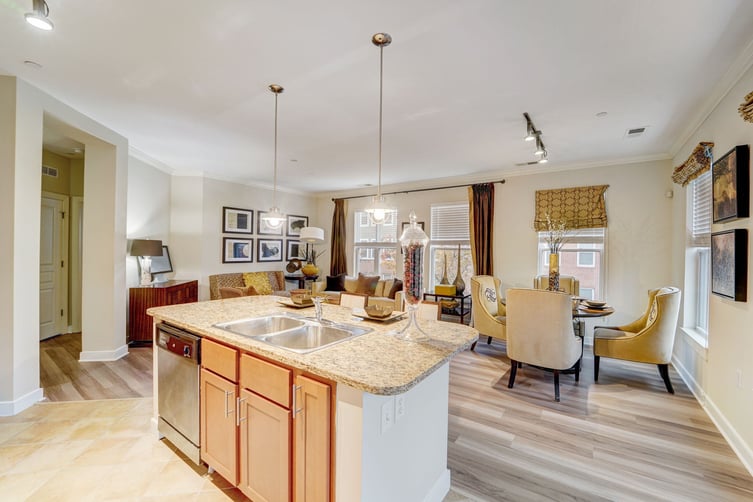
MCG Madison Ridge DST

- Asset Class: Multi Family
- Minimum: $100000
-
Financial Projections Only login member can access download






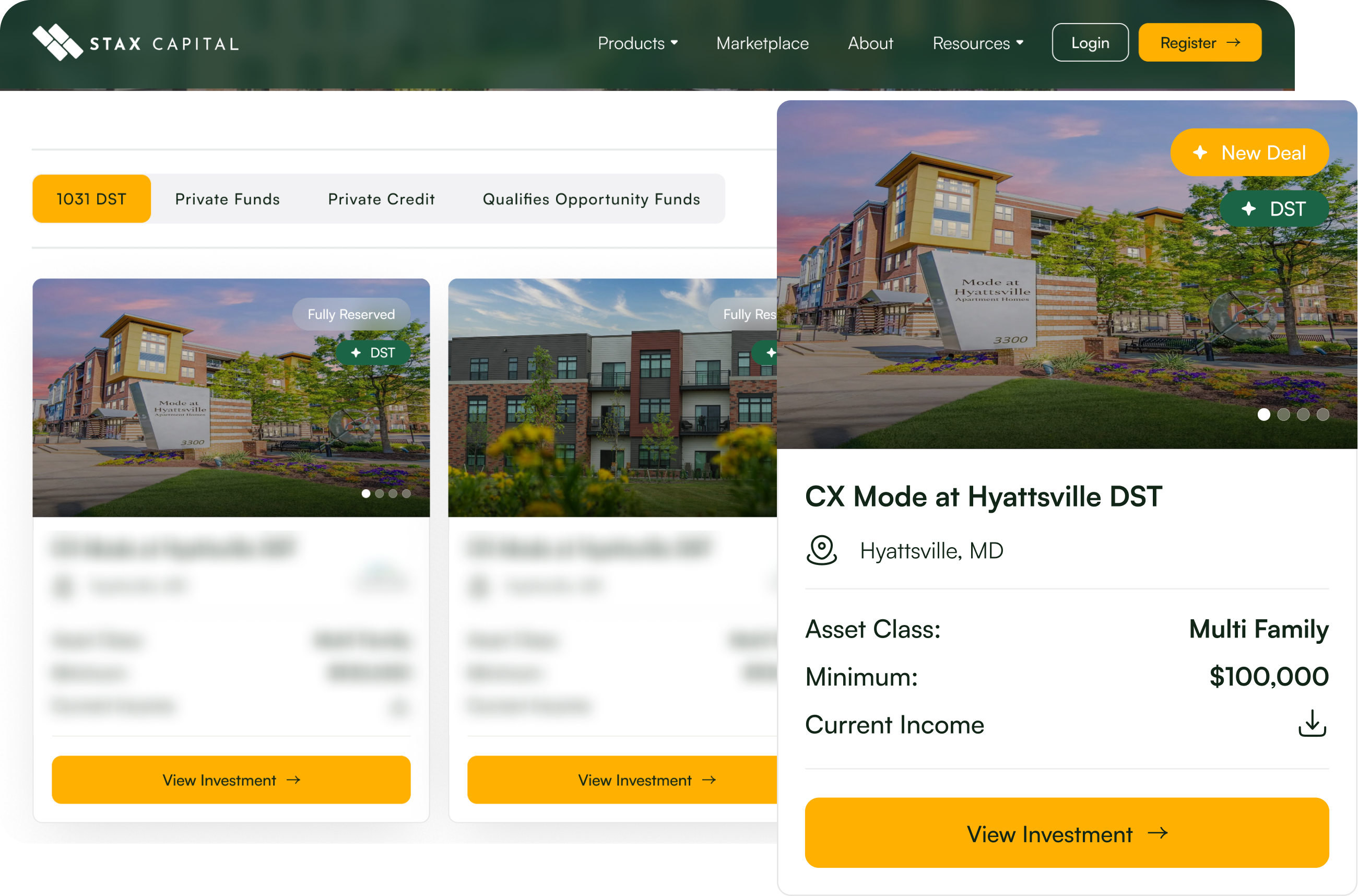
CX Mode at Hyattsville DST

- Asset Class: Multi Family
- Minimum: $100000
-
Financial Projections Only login member can access download
NexPoint Semiconductor Manufacturing DST

- Asset Class: Industrial
- Minimum: $100000
-
Financial Projections Only login member can access download
Focused on Quality, Designed for Passive Income
Explore exclusive DST investment options handpicked by industry experts. Each property is thoroughly reviewed for its income potential, enabling you to invest in real estate without hands-on management.
Explore our curated listings to find options that align with your financial goals and offer opportunities for tax-deferral and passive income.
Advanced Investment Analysis Tools
Use our platform to access in-depth property data and performance metrics, helping you confidently select DST investments that meet your unique strategy.
Comprehensive Data
Discover a wide selection of DST properties tailored to your strategy. As a registered user, you can view all available DST properties, empowering you to make informed decisions and build a diversified real estate portfolio.
New Investment Alerts
Get timely notifications about newly available DST properties. As a registered user, you'll receive early alerts, helping you seize investment opportunities before they’re widely available.
Educational Guides, Investor Resources and Monthly Newsletters
Gain full access to our expert-curated investment guides, resources, and newsletters. Stay informed with the latest industry trends, strategies, and updates tailored to your needs.
Download the Essential DST Guide
Learn everything you need about Delaware Statutory Trusts and how they fit your financial goals. Download the guide to see if DSTs align with your investment strategy.

Download the Essential DST Guide
Learn everything you need about Delaware Statutory Trusts and how they fit your financial goals. Download the guide to see if DSTs align with your investment strategy.

The 1031 Exchange Timeline
In a 1031 Exchange, you only have 45 days to identify a replacement property. Stax streamlines the process, guiding you through due diligence and transactional complexities to ensure you don’t miss key deadlines or tax benefits.
Day 1
Sale property or 1031 downleg transaction closed
.png?width=340&height=340&name=Layer_1%20(2).png)
Day 45
Identify replacement properties
.png?width=340&height=340&name=Layer_1%20(3).png)
Day 180
Deadline to complete the exchange
Market Insights
Dive into our curated insights to understand the market trends and investment opportunities that keep you informed and prepared for strategic financial decisions.
.png?width=826&height=502&name=What%20is%20a%20DST%20and%20can%20it%20qualify%20as%20a%201031%20replacement%20property%20(1).png)
- DST
What is a DST and can it qualify as a 1031 replacement property?
Andrew Carnaby's statement that 90% of millionaires build their wealth from real estate has become famous over time. Said at the turn of the century, this insight still holds true today.
Read More

- DST
Potential Benefits of Delaware Statutory Trusts for Investors
As an investor looking to diversify into real estate or expand your investments in properties, you may be wondering what the benefits of DST (Delaware Statutory Trusts) might be.
Read More

- DST
DST Exchange vs. 1031 Exchange: Key Differences and How They Work Together
Confused about whether to choose a Traditional or a DST 1031 exchange? Both are popular strategies offering potential tax benefits, but they also involve distinct risks and serve different goals. Understanding these differences is key to aligning your strategy with your financial objectives.
Read More
Stax at a Glance
At Stax, our extensive experience and industry partnerships provide access to exclusive private investment opportunities. From 1031 DST exchanges to private equity and credit, we deliver investment strategies backed by some of the industry's most trusted sponsors.
Learn MoreCombined Leadership Experience
35 YEARS
Private Investments Offered Through Stax
$12.3 BILLION
Our Sponsors Assets Under Management
$200 BILLION
Case Stories
Explore firsthand experiences of clients who have successfully transitioned to passive income, built wealth, and diversified their portfolios with our guidance.
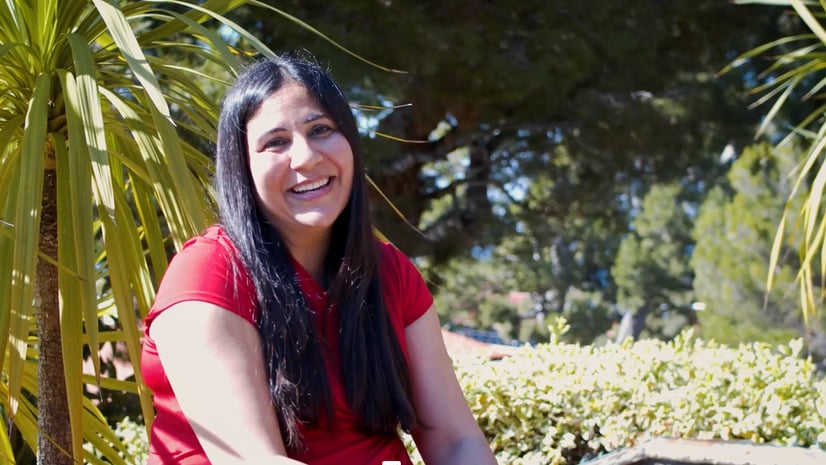

Stax made my transition to passive income smooth and stress-free.
Stax helped Shikha complete a 1031 exchange into DSTs, freeing her from property management and allowing her to focus on personal time.
-Shikha

Stax helped me shift to passive income and defer my taxes.
Stax guided Ramesh through a successful 1031 exchange and DST investments, allowing him to defer taxes and enjoy hassle-free income.
-Ramesh

Stax made it easy to switch to passive investments for our retirement.
Stax introduced Sima and Roman to DSTs, allowing them to shift from active property management to a hands-off strategy while maintaining a steady income.
-Sima and Roman
Disclosure
The experiences shared by clients of Stax Capital were given voluntarily without any compensation. These testimonials reflect individual opinions and are not intended as investment advice or guarantees of future results. Each investor should consider their own financial goals, risk comfort, and overall situation before making any investment choices.
Maximize Your Real Estate Investment with DST's
Unlock the potential of real estate investment without the hassle of management responsibilities. Delaware Statutory Trusts (DSTs) offer investors a unique opportunity to own a fractional interest in high-quality properties.
Benefits
Risks
Access larger investments
You get a fractional interest in large, high-quality assets like multi-family apartment complexes and self-storage units that would otherwise be out of reach, with an investment threshold as low as $100,000.
Get your time back
Exchanging into DST's allow for direct investment without the burden of property management. Properties are institutional grade and professionally managed by vetted and experienced sponsors.
Maximize your tax benefits
DST's offer access to properties of a size and scale that is typically unavailable to individual investors. Unlike standard TIC (tenancy in common) arrangements, DST's lower the investment threshold to as little as $100,000.
Receive passive income
DST structures and 1031 exchanges can retain benefits of real estate investment including potential cash flow, tax advantaged income, cost pass-throughs, depreciation and other tax benefits.
Difficult to Sell
There is no public market for DSTs, and one is unlikely to develop. Typical holding periods are 5 to 10 years, so you should be comfortable with a highly illiquid investment.
Fees and expenses
The DST structure includes various fees and expenses. As with any other investment, you should understand all fees and expenses prior to making your investment decision.
Lack of control
DSTs are professionally managed assets, and sponsors make all day-to-day and key operational decisions. Individual investors have no influence in the decision making process.
Subject to market risks
Like any real estate investment, DST cash flow levels and property values are subject to market, economic, tenant, and location risks. Projected cash flows are not guaranteed and can fluctuate over time.
Our Partners
Our network of industry-leading partners provides best-in-class investment managers, expert tax advisors, and solution-driven product developers. Together, we deliver exceptional investment solutions tailored to your needs.








Our Leadership Team
Our leadership team combines extensive knowledge of private markets with a shared dedication to putting clients first. We work closely with you, educating you on the pros and cons to ensure the decisions we help you make align with your long-term financial goals.
 Founder & CEO
Founder & CEO
Stacey Morimoto
i Due Diligence and Operations
Due Diligence and Operations
Quinn Morimoto
i Compliance Principal
Compliance Principal
Jason Finley
i
Stacey Morimoto
Mr. Morimoto leverages over 20 years of experience in the securities industry to help his clients navigate the complexities of alternative investments.
After starting his career at Salomon Smith Barney and recognizing the limitations of the traditional wirehouse platform, Stacey became an independent financial representative and established his own securities broker dealer.
Through DST investments, he saw a unique opportunity to deliver real value to clients that larger firms couldn’t offer. The ability to improve the overall day-to-day quality of people’s lives, beyond just their finances, is still what drives him.
With Stax Capital, a boutique firm that prioritizes individual attention, Stacey’s mission is to deliver the best possible educational experience for investors, so that they can make the right decision for themselves.

Quinn Morimoto
Son of founder and CEO Mr. Stacey Morimoto, Quinn has benefitted from early exposure to the inner workings of the securities industry. With a degree in finance from the University of San Diego, he heads up the due diligence and underwriting for all the DST offerings brought to the Stax Platform, a process that includes gathering appraisals, third party reports, and legal opinions as well as recreating sponsors’ financial models. He dives deep into the numbers and analyzes offers from every angle, looking for flaws, in order to minimize as much risk as possible for investors. Quinn has directly facilitated hundreds of private placement investment transactions and would say that the best part of the job is being able to truly make a lasting impact on people’s lives.

Jason Finley
With two decades of experience in sales and marketing across prestigious golfing, technology, and non-profit sectors, Mr. Finley has consistently embraced roles centered on helping others. He firmly believes that enjoying your work makes it effortless, which is why he cherishes being part of the Stax Capital family.
Educating investors on often-overlooked investment opportunities to help them grow their wealth, achieve tax efficiency, and plan for the future brings him immense satisfaction. From the onboarding process to discussing investment options, Jason is dedicated to ensuring every client receives the highest level of service when working with Stax Capital.
Jason is a graduate of the FINRA Institute at Georgetown Certified Regulatory and Compliance Professional (CRCP) program, further enhancing his expertise and commitment to providing exceptional service and compliance in the financial sector. He also holds the Series 22, 7, and 24 securities licenses, underscoring his comprehensive knowledge and regulatory compliance proficiency.
Hear from Our Clients & Industry Experts
Explore real-life success stories and get expert opinions on the value of 1031 DST exchanges and private market investments.
"Stacey and his team understand our needs and risk tolerance. When we have questions on current investments they're easily reached. I highly recommend them."
Julie Swail
Client
"The first time I met with Stax to discuss my options, I felt a level of comfort and security with their professionalism, their knowledge of the options that I could use, and their extreme sense of care in ensuring that my investments were as safe as possible but would also continue to grow as a legacy for my family."
Carol Deters
Client
"Stax Capital keeps impeccable due diligence compliance files that will protect issues in case of an examination. In addition, Stacey is a pleasure to work with in securities offerings."
Richard Weintraub
Securities Attorney
"I have been so impressed with Stax that as a 34-year Corporate Banker, I have proudly introduced Stax to past clients, colleagues, family and friends."
Paul Champlin
Client
"My exchanges were accomplished in a very timely and efficient manner. Thank you to Stacey, your colleagues and Stax Capital!"
Eric Lindquist
Client
"Stax deals with people with respect and patience and will never advise a client to pursue an investment which is not proper for them. Because of their experience, they are able to analyze properties, markets and companies that are best suited for their clients. They are a great resource to investors in real estate."
Paul Spring
President, Exchange Resources 1031
"I wanted to thank the Stax team for the incredible service that you provide to our customers. We all know that real estate transactions can be extremely stressful, especially when a 1031 exchange is involved – but your team comes through 'cool as a cucumber' every time. Your customer service, knowledge and strategic approach to investing in DST’s is off the charts!"
Stephen Decker
Qualified Intermediary
Disclosure
The experiences shared by clients of Stax Capital were given voluntarily without any compensation. These testimonials reflect individual opinions and are not intended as investment advice or guarantees of future results. Each investor should consider their own financial goals, risk comfort, and overall situation before making any investment choices.
Frequently Asked Questions
A Delaware Statutory Trust (DST) is a unique real estate investment vehicle that allows a group of individual investors to purchase fractional interests in large commercial real estate assets. These assets are typically beyond the financial reach of solo investors. Here’s how DSTs work and why they are relevant for real estate investors:
Formation and Sponsors:
- DSTs are created under Delaware trust law.
- Real estate companies (sponsors) form DSTs by identifying and acquiring assets using their own capital.
- The sponsor then opens an offering period, and individual investors purchase fractional shares of the DST.
- DST beneficiaries are passive investors, providing equity capital.
DST History:
- DSTs were established in 1988 with the passing of the Delaware Business Trust Act (later renamed the Delaware Statutory Trust Act in 2002).
Ownership Structure:
- DST investors, also known as beneficiaries, do not directly own physical real estate. Instead, they own shares of a trust specifically formed to be the legal owner of the underlying properties held within the trust.
- The legal separation between the trust and the pool of DST investors is crucial.
Yes, the IRS has approved Delaware Statutory Trust (DST) investments as like-kind property for 1031 exchanges. This approval allows investors to defer capital gains taxes by reinvesting the proceeds from the sale of appreciated real estate into DSTs. The key consideration is that the IRS treats each investor’s beneficial interests in a DST as direct property ownership, making it eligible for 1031 exchanges both when acquiring and selling the DST. However, it is critical to understand that if the DST sponsor fails to comply with IRS guidelines and requirements outlined in Revenue Ruling 2004-86 issued in 2004, the IRS may disqualify exchanges made in deficient structures. It is important to conduct diligence on each sponsor, their structure, review tax opinions related to each DST offering and talk with your tax and legal advisors prior to investing.
Filing taxes for Delaware Statutory Trust (DST) investments involves several considerations. Let’s break down the key aspects:
Beneficial Interest Ownership:
- DST investors acquire a fractional interest in the trust, making them “beneficial interest owners.”
- The IRS treats DSTs as “grantor trusts” disregarded for tax purposes.
- Beneficial owners report their share of income, expenses, and other tax-related items.
Income & Expenses Reporting:
- Instead of receiving Schedule K-1s or Form 1099s, DSTs issue grantor trust letters to beneficial owners.
- These letters detail the investor’s share of rental income, expenses, and other financial information.
- Beneficial owners report this information on IRS Schedule E or Form 1040, similar to reporting income from a single ownership rental property.
Phantom Income:
- Sometimes, a DST’s taxable rental income exceeds the actual distributions received due to “phantom income.”
- Phantom income can occur from rents received in advance or other factors.
- Investors should be aware of this when reporting income.
1031 Exchanges:
- DSTs qualify as like-kind replacement property for Section 1031 exchanges.
- Investors can defer capital gains taxes by reinvesting proceeds from the sale of real estate into DSTs.
Location and Tax Liability:
Remember that consulting with a qualified CPA or tax professional is essential to navigate DST tax obligations effectively.
In the Delaware Statutory Trust (DST) investment landscape, a broker-dealer plays a crucial role in marketing and selling DST offerings to investors. Let’s delve into the specifics:
DST Broker-Dealer:
- A DST broker-dealer is a securities company that specializes in selling investments related to DSTs.
- These broker-dealers collaborate with DST sponsors to market and distribute DST offerings to potential investors.
- To operate legally, the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) must license DST broker-dealers.
Due Diligence and Analysis:
- One of the primary functions of a broker-dealer is to analyze and perform due diligence on DST sponsor companies and their specific DST 1031 offerings.
- They assess the financial viability, structure, and overall quality of the DST investment opportunities.
- Some broker-dealers have in-house due diligence teams, while others may outsource this work to third-party providers.
Registered Representatives:
- Broker-dealers typically have a group of registered representatives who hold securities licenses with the broker-dealer.
- These representatives act as intermediaries between the broker-dealer and individual investors.
- They provide information, answer questions, and facilitate the investment process for clients interested in DSTs.
In summary, DST broker-dealers bridge the gap between DST sponsors and investors, ensuring that potential investors receive accurate information and have access to DST investment opportunities. Their due diligence helps investors make informed decisions about participating in DST offerings.
When evaluating potential parties for Delaware Statutory Trust (DST) investments, ensuring their reputation and trustworthiness is crucial. Here are some essential steps to help you identify reputable DST sponsors and advisors:
Research the DST Sponsor:
- DST sponsors are responsible for setting up the trust that holds real estate assets.
- Investigate the sponsor’s history, track record, and experience in managing DSTs.
- Look for sponsors with a successful track record of underwriting, financing, property acquisition, and ongoing management.
Check for Transparency:
- Transparency is key. Ensure that the sponsor provides detailed information about the investment property, including financial performance, management team, and exit strategy2.
- Ask about any affiliations between the DST advisor and sponsor. Some advisors may be sponsor-affiliated, which could impact their recommendations3.
- If the relationship between the DST advisor and sponsor lacks transparency, inquire further to understand the connection.
Avoid Conflicts of Interest:
- Be cautious of sponsor-affiliated advisors who may prioritize specific deals or offerings from a single sponsor.
- Independent advisors (not affiliated with a specific sponsor) may provide more objective advice.
- Ask whether the advisor offers deals from multiple sponsors or just one. Ensure they act in your best interest3.
Due Diligence on Advisors:
- Evaluate advisors beyond licensure. Consider their expertise, risk assessment, and understanding of your investment goals.
- Reputable advisors are transparent about their commissions and fees.
- Use resources like FINRA’s BrokerCheck to verify where DST sponsors and advisors are registered
References and Background Checks:
- Check references and verify employment history for both sponsors and advisors.
- Conduct background checks to ensure credibility and reliability
Remember that due diligence is essential when choosing reputable parties for DST investments. Seek professional advice and thoroughly assess the sponsor’s and advisor’s qualifications before making investment decisions.
Assessing the quality of a Delaware Statutory Trust (DST) investment involves thorough analysis and consideration of several factors. Here are key steps to help you evaluate DST opportunities:
Property Quality and Location:
- Examine the underlying real estate property held by the DST. Consider factors such as location, property type (e.g., office, retail, multifamily), and market demand.
- A well-located property in a strong market with stable or growing rental income is generally preferable.
Sponsor Reputation and Track Record:
- Research the DST sponsor’s history and experience. Look for sponsors with a successful track record in managing DSTs.
- Consider their ability to acquire, manage, and exit properties effectively.
Financial Performance:
- Review financial statements, including income and expense reports provided by the sponsor.
- Assess the property’s historical performance, projected cash flow, and potential for appreciation.
- Evaluate the stability of rental income and any potential risks (e.g., lease expirations, market fluctuations).
Tenant Quality and Leases:
- Understand the tenant mix. Are there creditworthy tenants with long-term leases?
- Evaluate lease terms, rent escalations, and tenant stability.
- Vacancy rates and tenant turnover can impact cash flow.
Exit Strategy:
- Consider the sponsor’s exit plan. How will the property be sold?
- Understand the timeline for potential liquidity events.
- DSTs typically have a finite holding period (often 7 to 10 years).
Tax Implications:
- Consult with a tax advisor to understand the tax benefits and implications of DST investments.
- DSTs are commonly used for 1031 exchanges, allowing investors to defer capital gains taxes.
Risk Tolerance and Investment Goals:
- Assess your own risk tolerance and investment objectives.
- DSTs are generally considered passive investments, so be prepared for limited control over property management decisions.
Due Diligence and Professional Advice:
- Conduct thorough due diligence. Read offering documents, legal agreements, and sponsor materials.
- Seek advice from professionals, including real estate attorneys, CPAs, and financial advisors.
Remember that each investor’s situation is unique, and what constitutes a quality DST investment may vary based on individual goals and preferences. Always make informed decisions and seek professional guidance.
The monthly cash flow from Delaware Statutory Trust (DST) investments is not guaranteed. Here’s why:
Passive Investment Structure:
- DSTs are typically structured as passive investments.
- Investors contribute capital to the DST but do not actively manage the property.
- Cash flow depends on the performance of the underlying real estate asset.
Rental Income Variability:
- DSTs primarily generate cash flow from rental income (e.g., from commercial properties, apartment complexes, etc.).
- Rental income can fluctuate due to factors such as vacancies, lease renewals, and market conditions.
- If tenants vacate or lease rates decrease, it directly impacts the cash flow.
Property-Specific Risks:
- Each DST property has its own unique risks.
- Factors like location, tenant quality, property management, and market trends affect cash flow.
- Unexpected expenses (e.g., repairs, maintenance) can reduce available cash flow.
Market Conditions and Economic Cycles:
- Economic cycles impact real estate markets.
- During economic downturns, rental demand may decrease, affecting cash flow.
- Conversely, strong market conditions can lead to stable or increasing cash flow.
Loan Payments and Debt Service:
- DSTs often use financing (mortgages) to acquire properties.
- Loan payments (debt service) reduce available cash flow.
- Investors receive their share of cash flow after deducting debt payments.
Distribution Timing:
- DSTs distribute cash flow periodically (e.g., monthly or quarterly).
- The timing and amount of distributions depend on property performance and lease terms.
Risk Disclosure:
- DST offering documents provide detailed risk disclosures.
- Investors should carefully review these documents before investing.
In summary, while DSTs offer tax benefits and passive ownership, cash flow is subject to various factors. It is essential to assess each DST opportunity thoroughly and understand the associated risks. Consult with financial professionals to make informed investment decisions.
The Debt Service Coverage Ratio (DSCR) is a critical metric when evaluating an investment in a Delaware Statutory Trust (DST) property with an associated loan. Let us explore why it matters:
Definition of DSCR:
-
- The DSCR measures the property’s ability to cover its debt obligations (loan payments) using its net operating income (NOI).
Importance of DSCR:
- Risk Assessment: A high DSCR indicates that the property generates sufficient income to cover its debt payments comfortably. Conversely, a low DSCR suggests higher risk.
- Lender Requirements: Lenders often require a minimum DSCR to approve a loan. If the property’s DSCR falls below their threshold, financing may be denied.
- Investor Protection: A healthy DSCR provides a buffer against unexpected expenses or fluctuations in rental income. It safeguards investors from default risk.
Interpretation:
-
- A DSCR of 1.0 means the NOI exactly covers debt payments. Ideally, investors prefer a DSCR above 1.2 or 1.25.
- A DSCR below 1.0 indicates insufficient income to cover debt, which is risky.
- Higher DSCR values indicate stronger financial health.
Considerations:
- Conservative Approach: Some investors aim for a higher DSCR to mitigate risk. They seek properties with substantial NOI relative to debt payments
- Property-Specific Factors: Consider the property type, location, and market conditions. Different property types may have varying acceptable DSCR thresholds.
Due Diligence:
-
- When evaluating a DST investment, review the sponsor’s projected DSCR for the property.
- Understand how the sponsor calculated NOI and debt service.
- Assess the impact of potential changes (e.g., vacancies, rent adjustments) on the DSCR.
-
In summary, a healthy DSCR is essential for the financial stability of a DST investment. It ensures that the property generates enough income to meet its debt obligations and provides confidence to both investors and lenders.
Broker Check is a valuable tool provided by the Financial Industry Regulatory Authority (FINRA) that allows investors to research the professional backgrounds of investment professionals, brokerage firms, and investment adviser firms. Here is why it is crucial to use BrokerCheck:
Transparency and Informed Decisions:
- BrokerCheck provides transparency by offering detailed information about financial professionals.
- Before making any investment decisions, it is essential to review this information to ensure you are working with a reputable and trustworthy professional.
Investment Professional Histories:
- By using BrokerCheck, you can find an investment professional’s history.
- It includes details such as employment history, qualifications, industry exams passed, and any customer disputes or disciplinary events on their record.
Barred Brokers:
- BrokerCheck helps you determine if any brokers have been barred by FINRA.
- If a broker has regulatory actions or has been involved in fraudulent activities (such as a Ponzi scheme), this information will be available in their BrokerCheck report).
In summary, BrokerCheck empowers investors to make informed decisions by providing insights into the backgrounds and qualifications of financial professionals. It is a crucial step in vetting potential advisors and safeguarding your investments.
- Initial Fees: These cover the setup and administrative costs of the DST. They may include legal fees, due diligence expenses, and other upfront charges.
- Closing Costs: Similar to traditional real estate transactions, DSTs involve closing costs. These include escrow fees, title charges, and other expenses related to finalizing the investment.
- Property Management Fees: DSTs typically hire professional property management companies to handle day-to-day operations. Investors pay fees for these services, which cover tasks like tenant management, maintenance, and repairs.
- Sales Commissions: When you invest in a DST, the sponsor or broker may charge a sales commission. This fee compensates them for facilitating the investment.
- Other Expenses: Depending on the specific DST, there may be additional costs, such as appraisals, environmental reports, and property condition assessments
Connect
With Us
Our personalized approach ensures that we thoroughly understand your unique circumstances, aspirations, and any queries you may have. Whether you choose to fill out the form below or give us a call, rest assured that you’ll receive a prompt response and expert guidance.
