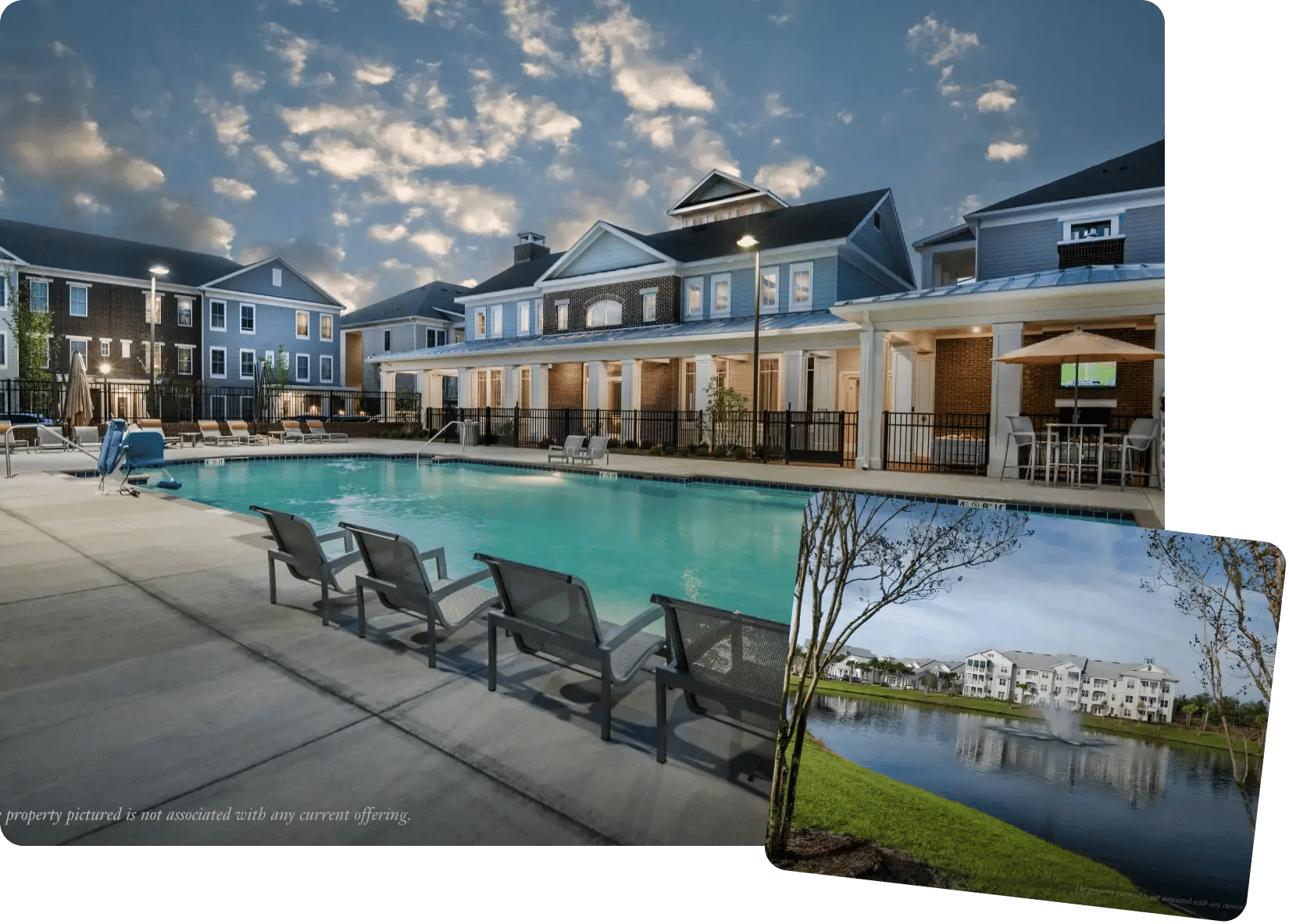
Explore the Private Markets Leaders in DST, 721, & 1031
With over 35 years of expertise, we guide investors on 1031 DST exchanges and Private Market Investments. Learn how these opportunities can enhance tax benefits, create passive income, and drive portfolio growth.
Our Partners
Our trusted partners include top investment managers, tax advisors, and product developers, offering tailored solutions to meet your investment goals.
.png?width=471&height=160&name=image%2016%20(1).png)






.png?width=471&height=160&name=image%2016%20(1).png)






Our Products
Discover a range of investment options, including 1031 & 721 DSTs, Private Real Estate Funds, Private Credit, and Qualified Opportunity Funds.

A Hassle-Free 1031 Solution
Defer capital gains taxes and diversify your portfolio with Delaware Statutory Trust (DST) investments. Our thoroughly vetted DST 1031 investment opportunities offer access to high-quality real estate with the potential for income, growth, and powerful tax benefits.

721 Exchange
Unlock institutional real estate access through a 721 Exchange. This tax-deferred strategy allows property owners to exchange real estate for REIT operating units, providing passive income potential, diversification and enhanced liquidity.

Direct Participation Programs
Our Private Funds and Private Equity Real Estate Investments offer unique opportunities in carefully selected sectors. Backed by thorough due diligence, these funds offer growth and income opportunities at various points along the real estate life cycle.

Direct, Non-Bank Lending
Access income-generating potential through our private credit investment offerings. Our team connects you with experienced managers in the private credit space. These investments are supported by thorough financial analysis and risk management.

A Tax Deferral and Elimination Strategy
Take advantage of one-of-a-kind tax incentives with Qualified Opportunity Funds. These funds let you defer and eliminate capital gains taxes, all while investing in community-driven projects. You can enjoy tax deferral and tax-free gains while making a social impact.
Current Investments
We frequently launch new investment products to help meet various financial goals. Sign up for alerts, newsletters, and early access to opportunities.
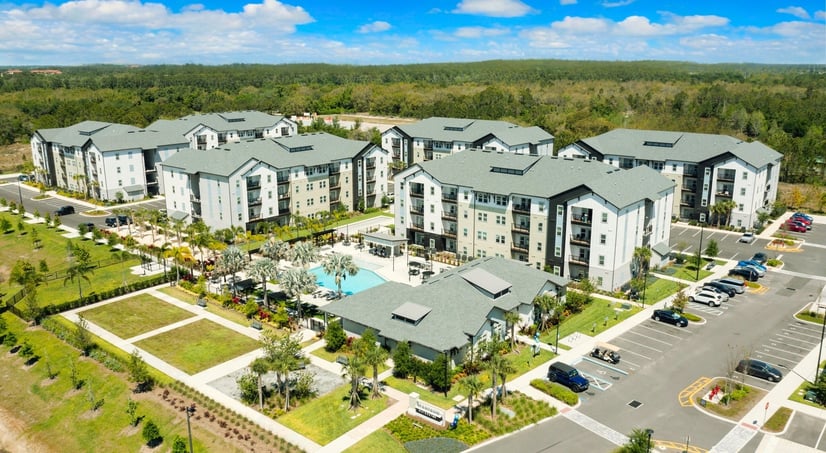
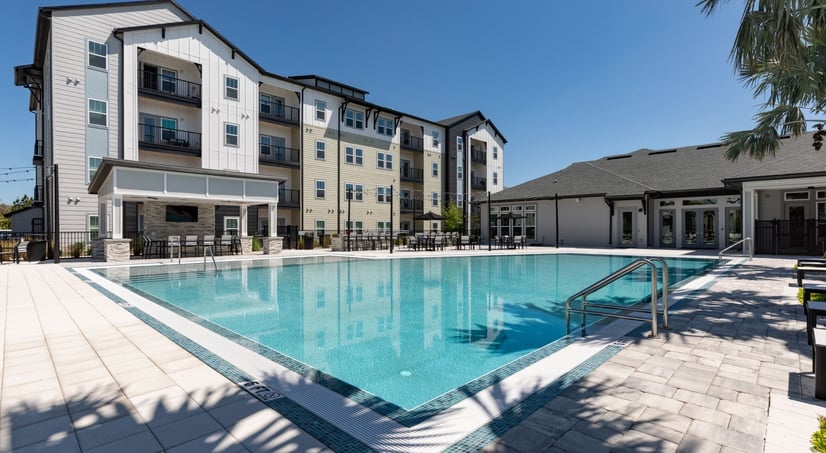







MCG Waterstar DST

- Asset Class: Multi Family
- Minimum: $100000
-
Financial Projections Only login member can access download
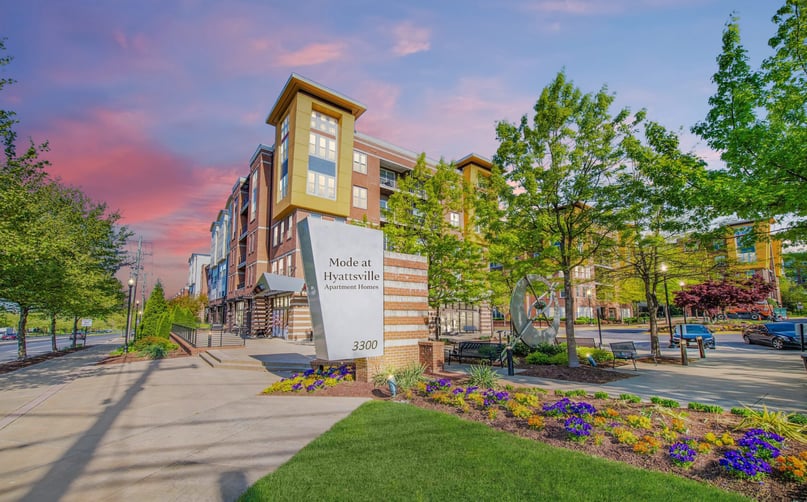






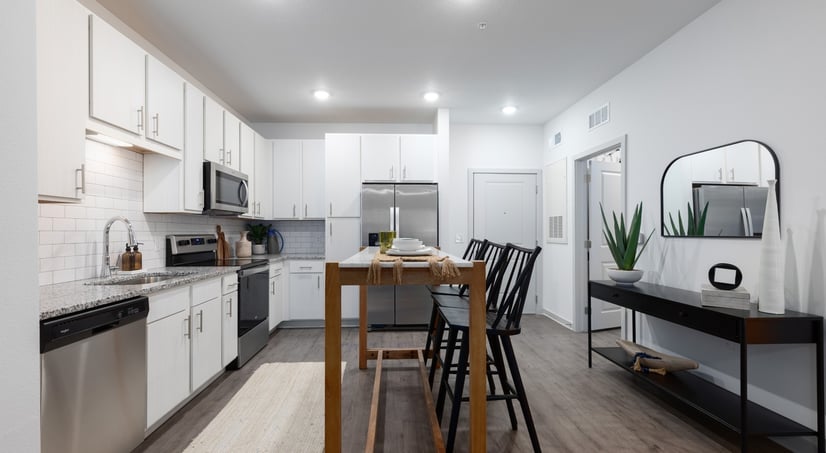
CX Mode at Hyattsville DST

- Asset Class: Multi Family
- Minimum: $100000
-
Financial Projections Only login member can access download
NexPoint Semiconductor Manufacturing DST
- Asset Class: Industrial
- Minimum: $100000
-
Financial Projections Only login member can access download
How to Get Started
Getting started is easier than you think. Just search, select, and click invest – we’ll handle the rest to help ensure your financial objectives are met.
Search Our Marketplace
Start by exploring our curated marketplace. You’ll find a wide range of thoroughly vetted investment opportunities. From 1031 DSTs to Private Funds, our marketplace offers detailed insights to help you make informed decisions.
Choose Your Investments
Once you've reviewed your options, select the investments that align with your financial goals. Whether it’s one or multiple DST properties or non-1031 alternatives, our team is available to answer any questions and help guide you through the process.
Start Investing
With your investments selected, you’re ready to take the next step. Our seamless process makes it easy to invest and begin building your portfolio. From onboarding to ongoing support, we’re with you every step of the way.
Tap Directly Into Our Deep Expertise
We stand out by focusing on precision, diligence, and client commitment. Partnering with top managers, we offer select Delaware Statutory Trusts and Private Market Alternatives. Our leadership provides expert guidance through regulatory and market changes.


Powerful Investments
Private Market Alternatives, like DSTs and private equity real estate, provide the potential for diversification, income, growth, and significant tax advantages with minimal correlation to traditional assets.
.png?width=60&height=60&name=magnifying-glass-plus-duotone-solid%201%20(1).png)
Rigorous Due Diligence
We apply a proprietary due diligence process to evaluate managers and products, using financial analysis and risk assessment to identify promising investment opportunities with strong return potential.
Thoughtful Guidance
Our experienced professionals provide tailored advice and insights to support your evolving financial journey, helping you make informed investment decisions today and plan confidently for the future.
Transaction Management
Our team supports every aspect of your investment transactions, from product reviews to purchases, ensuring compliance and delivering a smooth, efficient experience.
Investing Guides
Delve into alternative investments with our comprehensive guides. Acquire foundational knowledge on 1031 exchanges, Delaware Statutory Trusts (DSTs), Private Credit, Qualified Opportunity Funds, and additional topics. Obtain the insights necessary for success.
- DST
Understanding 1031 & DST Exchanges
Unlock the benefits of tax-deferred real estate investing with our comprehensive guide to 1031 and DST exchanges.
Download- 1031 Exchange

What Every Investor Should Know About 1031 Exchanges
Discover essential insights into 1031 exchanges, including key rules and strategies every investor should know.
Download- QOZ Funds

Qualified Opportunity Zone Funds Explained: A Guide for Real Estate Investors
Explore how Qualified Opportunity Zone Funds can provide unique tax benefits and support growth in designated areas.
Download- Private Funds

Understanding the Essentials of Direct Participation Programs
Discover the fundamentals of Direct Participation Programs (DPPs) in private funds. Learn how they work, their advantages, and potential risks.
Download- Private Credit

Navigating Private Credit Funds: A Beginner’s Guide
Explore the world of private credit funds with this easy-to-understand guide. Discover how these funds operate and how they can diversify your investment portfolio.
Download- 721

Understanding the 721 Exchange: A Path to Diversification and Passive Income
Explore the 721 exchange process, its benefits, and how it compares to traditional 1031 exchanges in optimizing real estate portfolios.
Download
Investor Resources
Explore our investor resources, including blogs, podcasts, videos, testimonials, and calculators. Our tools are designed to assist you in making informed decisions by offering unique insights into the products and services offered here at Stax.

Top 7 Questions to Ask Before Investing in a DST
Investing Through a DST? Ask These 7 Questions to Uncover Hidden Risks Before You Sign.
When evaluating a Delaware Statutory Trust (DST) as part of your 1031 exchange strategy, it's essential to ask informed questions to ensure the investment aligns with your goals, risk tolerance, and timeline.
Here are the Top 7 Questions to Ask Before Investing in a DST.
What is a DST?
Delaware Statutory Trusts (DSTs) offer investors the opportunity to hold fractional interests in professionally managed commercial properties. This structure facilitates passive real estate investment while potentially delivering tax advantages through a DST 1031 exchange. Additionally, DSTs provide investors with limited liability and exposure to a diverse range of commercial real estate assets.
1. What is the Sponsor’s Track Record and Due Diligence Process?
Real estate investing requires you to evaluate the sponsor’s experience and performance. Ask about their previous offerings and how those investments performed over time. Review their financial stability and operational track record to assess reliability. Understand the due diligence process they follow, including steps like site visits, stress testing, and background checks.
Also, consider the level of due diligence conducted by Stax to ensure added transparency and confidence in the offering.
2. What Are the Specific Risks Associated with the DST?
DSTs offer attractive benefits such as passive income and potential capital gains. But they come with inherent risks such as illiquidity. As we know that interests in DSTs cannot be easily sold or traded, they limit the ability to exit the investment before the end of the term. Real estate market fluctuations can also impact the performance of the asset, potentially affecting both returns and capital value. Tenant turnover and occupancy issues may result in inconsistent income.
Additionally, conflicts of interest could arise between the sponsor and the accredited investors if their objectives are not fully aligned. It is one of the important things to consider while investing in real estate.
3. What Is the Investment Objective and Exit Strategy?
It is important to have a clear understanding of the investment objective and exit strategy of the DST before making a commitment. Identify whether the primary goal is to generate consistent income, seek long-term appreciation, or a combination of both. Clarify the typical hold period, as this can impact your liquidity and overall planning.
Additionally, review the available exit options, which may include an asset sale, a 721 exchange into a REIT, or other structured outcomes. Knowing what happens at the end of the trust’s term is essential for setting expectations and preparing for next steps in your investment journey.
4. How Does This DST Fit Within My 1031 Exchange Timeline?
The 1031 exchange process comes with strict deadlines that must be adhered to for successful completion. Investors are given 45 days to identify a replacement property and must close within 180 days. It is crucial to confirm that the DST can be acquired within this timeframe to avoid missing key deadlines.
Stax is committed to helping investors meet these requirements, offering support for timely closings. When properly planned, Stax can assist in completing the 1031 exchange process within just 3–5 business days, and provides an attractive option for portfolio diversification.
5. What Are the Fees and How Will They Impact My Return?
DST investments may involve several types of fees, each of which can affect the overall performance of the investment. These fees typically include upfront costs, asset management fees, and disposition or backend fees, which are incurred when the asset is sold. It is crucial to fully understand both the disclosed fees and any embedded fees that may not be immediately apparent.
Carefully assess how these costs will impact the net cash flow and the long-term returns of the investment. By doing so, investors can make more informed decisions and better evaluate the true value of the DST.
6. What Kind of Real Estate Is Held in the DST and Where Is It Located?
Understanding the asset type is crucial when evaluating a DST investment. Whether the property is multifamily, industrial, retail, or another category, each type has its own set of characteristics and risks. It is important to request detailed information about the location, including demographics, employment trends, and the overall economic stability of the market.
These factors help assess the growth potential and risks associated with the investment. Additionally, evaluate the quality of the property, the tenant mix, and the lease structures in place. These elements are critical as they directly influence both the performance of the asset and the level of risk involved in the investment.
7. Am I Eligible, and Is This Investment Suitable for My Goals?
You may be eligible for a DST (Delaware Statutory Trust) investment if you're an accredited investor. Also, if you're completing a 1031 exchange to defer capital gains taxes. DSTs are commonly used in real estate 1031 exchanges as replacement property options.
This type of investment may be suitable if you're seeking passive real estate income without the responsibilities of being a landlord, want diversification across institutional-quality properties, are looking to defer taxes through a 1031 exchange, and have a desire for potential cash flow.
However, a DST may not be appropriate if you require liquidity, as these investments are generally illiquid for 5 to 10 years. Also, if you want control over property management, have a short-term investment horizon, or are uncomfortable with real estate market risks then DSTs might not be suitable for you.
Is DST Investing Right for You?
While DST investments provide an attractive option for diversifying your portfolio, they come with risks. It’s essential to weigh these risks against the potential rewards and ensure you’re prepared for the long-term commitment. By working with qualified professionals and thoroughly understanding the terms and implications, you can make informed decisions that align with your financial goals.
If you’re ready to take the next step or need guidance, we’re here to help. Get in touch with Stax today to learn more about how DST investments fit into your strategy!

Qualifying for a 1031 Exchange: Common Mistakes to Avoid
Navigating a 1031 exchange? Avoid these common mistakes to keep your tax deferral intact.
While a 1031 exchange can defer capital gains taxes, the rules are strict. Missteps with timelines, property value, or fund handling can lead to disqualification. Careful planning helps avoid them.
This guide will help you steer clear of the most frequent pitfalls that could jeopardize your eligibility for a 1031 Exchange.
What is a 1031 Exchange?
A 1031 exchange is a tax strategy under Section 1031 of the Internal Revenue Code. It allows investors to defer capital gains taxes when selling a business or investment property. To qualify, the proceeds must be reinvested into a like-kind property of equal or greater value. It helps investors grow their wealth by keeping gains in a tax-deferred state.
Common mistakes to avoid
Mistake #1: Not using a Qualified Intermediary (QI)
A Qualified Intermediary (QI) is a neutral third party. They are required for a valid 1031 exchange. The QI holds the sale proceeds and uses them to buy the replacement property. This keeps the process in line with IRS rules.
If you access the funds yourself, the exchange no longer qualifies. That means you’ll owe capital gains taxes right away. Not using a QI can turn a tax-deferred opportunity into a taxable mistake. Always work with a QI who specializes in 1031 exchanges.
Mistake #2: Not sticking to the timeline
It is imperative to follow the 45-day and 180-day timelines. A 1031 Exchange strictly enforces a 45-day identification period, during which the investor must identify potential replacement properties. Additionally, you have 135 days to close on the purchase of the replacement property.
If you miss any part of the timeline, you forfeit the opportunity to receive tax deferral benefits.
The IRS provides three identification rules—the 3-Property Rule, 200% Rule, and 95% Rule—to guide the selection of new investments. These rules are designed to offer flexibility in your property choices. If something goes wrong with your first option, you’ll have backups ready. However, these timelines must be strictly adhered to.
- 3-property Rule - The 3-Property Rule in a 1031 exchange lets you list up to three potential replacements, offering flexibility if one falls through. However, if none are acquired within 180 days, you lose tax deferral benefits.
- 200% Rule -The 200% Rule in a 1031 exchange lets you identify unlimited replacement properties, as long as their total value doesn’t exceed 200% of the sold property’s value. For a $500,000 sale, identified properties can’t exceed $1 million to maintain tax deferral eligibility.
- 95% Rule - The 95% Rule in a 1031 exchange allows unlimited property identification with no value cap, but you must acquire at least 95% of the total value to qualify. It’s most effective when buying a full portfolio from one seller, provided all IRS requirements are met.
Mistake #3: Incorrectly identifying replacement property
Finding the right replacement property is essential to qualify for a 1031 Exchange. The property must be “like-kind”—not necessarily identical, but it must be held for business or investment purposes. Residential property held for personal use does not qualify under this category.
A trustworthy Qualified Intermediary (QI) can assist you in finding the right property. Keeping the three identification rules in mind can also help you make the most of a 1031 Exchange. This guidance is not based on your capital gains situation.
Mistake #4: Incorrect Ownership Structures
Owning property through partnerships or LLCs without proper planning can disqualify your 1031 Exchange. The IRS requires the same taxpayer to sell and buy. If it happens that partners split or restructure ownership mid-exchange, you risk losing deferral benefits.
A Delaware Statutory Trust (DST) can be used as a 1031 replacement property, offering fractional ownership in institutional-grade real estate, and is often suitable for those seeking to move toward passive ownership.
Alternatives like DSTs (Delaware Statutory Funds) offer flexibility. They let investors part ways or reinvest individually if a need emerges mid ownership. It helps you stay compliant and protect your tax advantage.
Note: If a property is owned through a partnership or LLC, and one or more partners want to cash out or change ownership before reinvesting then a properly planned drop out or conversion to TIC/DST must be done in advance.
Mistake #5: Documentation and Form errors
Proper documentation and adherence to the timeline are non-negotiable to qualify for a 1031 Exchange. Some of the key documents include the signed sales contract, completed 1031 Exchange information sheet, exchange agreements, settlement statements, and documentation related to closing day and escrow setup.
Note: You must seek assistance from your Qualified Intermediary (QI) in preparing these documents to avoid any errors.
Mistake #6: Identifying just one property - must identify 3-4 properties
Limiting yourself to just one replacement property during a 1031 Exchange is risky. If that deal falls through, you could lose your eligibility for tax deferral. The IRS allows you to identify up to three properties—take advantage of that flexibility.
Identifying 3–4 options provides a safety net and increases your chances of successfully completing the exchange within the strict timeline. Always plan for backups.
Mistake #7: Debt Replacement Mistakes
Many believe you must match or exceed the loan amount from the sold property. That’s false. The key is replacing the value of the debt—not the loan itself. If you had $400,000 in debt, you can replace it with cash, seller financing, or private funds.
Using less than the full value can trigger taxes. Don’t assume another loan is your only option. Mixing funding sources is fine. Always consult a tax professional to avoid costly mistakes and ensure full tax deferral.
Ready to start your 1031 Exchange Journey
Successfully qualifying for a 1031 exchange often comes down to following key IRS rules—such as meeting strict timelines, choosing eligible properties, and using a qualified intermediary. Paying close attention to these requirements can greatly improve your chances of deferring taxes and preserving your investment gains.
With careful preparation and informed decisions, investors put themselves in a strong position to meet 1031 exchange criteria. For those exploring this route, understanding the process can be a valuable first step toward potential tax deferral benefits.
If you’re ready to start your 1031 exchange journey or need expert advice, get in touch with us today!

Unlocking Qualified Opportunity Zone Tax Benefits: What Investors Should Know
Did you know you may be missing out on potential tax advantages available through Qualified Opportunity Zones, depending on your unique situation and eligibility? Many investors overlook Qualified Opportunity Zones (QOZs) simply because they don’t understand how they work.
However, these federally designated areas offer powerful tax advantages, including the ability to defer tax on capital gains, reduce taxable income, and even eliminate capital gains tax on long-term investments.
This guide will simplify QOZs and help you leverage them for federal income tax purposes and long-term wealth growth.
What Are Qualified Opportunity Zones?
Qualified Opportunity Zones (QOZs) were established under the 2017 Tax Cuts and Jobs Act to drive economic development and job creation in underserved communities. Investors can place capital gains and qualified 1231 gains into a Qualified Opportunity Fund (QOF)—an investment vehicle that files either a corporate federal income tax return or partnership return—offering multiple tax advantages.
To qualify, investments must be made in a Qualified Opportunity Zone Business (QOZB) or Qualified Opportunity Zone Business Property (QOZBP). The Internal Revenue Service (IRS) oversees these programs, ensuring investments are compliant with tax regulations.
Key Tax Benefits of Investing in QOZs
Investing in a Qualified Opportunity Zone (QOZ) isn’t just about building wealth—it’s also about unlocking powerful tax advantages. Here’s how investors can benefit:
Defer Capital Gains Taxes
One of the biggest tax perks of investing in a QOZ is the ability to delay paying taxes on capital gains. If you’ve made a profit from selling a business, stocks, real estate, or even collectibles like rare art, you can reinvest those gains into a Qualified Opportunity Fund (QOF) and push your tax bill to the end of 2026. However, you must invest within 180 days of selling your asset.
This rule has a few exceptions. If your gains come from a partnership, S corporation, estate, or trust, the 180-day period can start on the last day of the taxable year, the entity’s own 180-day deadline, or its tax return due date.
There’s one catch: if you sell your QOF shares before 2026, you’ll owe taxes right away. Plus, your original tax rate stays the same—short-term gains remain short-term, and long-term gains remain long-term. While this deferral won’t lower your tax rate, it buys time and allows you to reinvest more capital upfront.
No Capital Gains Tax on Growth
The biggest reward for long-term investors is the chance to benefit from tax exclusions on the growth of their QOZ investment. If you hold your investment for at least 10 years, any appreciation you earn is tax-free when you sell.
Most tax deferral programs only delay taxes—but QOZs can let you eliminate capital gains taxes on appreciation if all IRS requirements are met, including a 10-year holding period and proper fund compliance. Even after the QOZ program technically expires in 2026, you can still enjoy tax-free growth until 2047 as long as your investment stays in a QOF.
This may be a significant advantage for long-term investors, especially in zones with favorable economic trends. However, outcomes vary, and market conditions can shift. If your investment increases significantly, you could reduce your tax burden, though savings depend on appreciation, fund performance, and future tax law changes.
Shelter Income from Taxes
If you invest in real estate through a QOF, you can also reduce taxes on income generated by your property. Once the property is fully developed or renovated and has steady tenants, it will start producing rental income.
Thanks to depreciation, a key tax benefit in real estate, your taxable income can be much lower than your actual earnings. Depreciation accounts for wear and tear, reducing reported profits while keeping more money in your pocket.
For example, if your rental property earns $70,000 per year but has $30,000 in depreciation expenses, you only pay taxes on $40,000. This tax break allows investors to keep more of their earnings while still benefiting from real estate appreciation.
No Depreciation Recapture Tax
Depreciation is a double-edged sword. While it lowers taxable income during ownership, investors outside of QOZs must pay a hefty depreciation recapture tax—usually 25%—when selling their property.
But QOZ investors who hold their properties for 10+ years don’t have to pay this tax. Even though they’ve benefited from depreciation deductions, they may avoid the typical depreciation recapture tax, which can enhance net proceeds. As with all tax benefits, this is subject to eligibility and IRS compliance.
Excess Depreciation Can Offset Other Investments
In some years, a real estate investment may not generate much net income—especially during the early stages when occupancy is still ramping up. During these low-profit years, depreciation may exceed the income the property generates.
When this happens, investors can carry forward excess depreciation to offset future income. In some cases, they can even use these losses to lower taxes on other passive investments. However, this tax benefit depends on the investor’s ability to track and use these excess deductions properly.
Long-Term, Tax-Free Cash Flow
While many investors may choose to sell their QOZ investments after 10 years, others can keep earning tax-free cash flow until 2047. However, not all funds are structured to last that long, so it’s important to choose the right QOF with a long-term strategy.
This extended tax-free growth period may offer advantages depending on fund structure and market conditions. If a fund decides to sell a property early, investors might not be able to take full advantage of this tax-free window. That’s why choosing the right fund manager with a strong long-term vision is crucial.
Ready to Take Advantage of QOZ Tax Benefits?
Qualified Opportunity Zones can be a powerful tool for long-term investors with capital gains. By deferring taxes, benefiting from depreciation, and potentially eliminating future capital gains, these investments offer flexibility and upside—when managed correctly.
Want help evaluating whether a QOZ fits your goals? Let’s talk. Our team can walk you through the timelines, structures, and strategies designed for accredited investors seeking efficient ways to grow their wealth.

Interest Rates & Real Estate Investing: Here's What You Need to Know
Think interest rates don’t matter? Think again. A small change in prevailing interest rates can significantly affect mortgage payments, which may impact an investor’s cash flow and returns. If you want to succeed in real estate, you need to understand how these shifts affect your investment property and overall return on investment.
In this article, we’ll break it all down in simple terms and give you actionable investment strategies to navigate a shifting market and optimize your investment approach.
What Are Interest Rates & Why Do They Matter?
Interest rates are the price you pay to borrow money. When you take out a mortgage, the lender adds interest on top of the amount you borrowed. The higher the rate, the more you pay over time.
For real estate investors, even a small rate increase can make a big difference. A lower interest rate keeps costs down and increases your return on investment (ROI). A higher rate can make an investment property less attractive by raising monthly payments.
Knowing how interest rates work helps you make smarter decisions. Whether you’re buying your first rental or expanding your portfolio, staying informed gives you an edge.
How Do Interest Rates Affect Real Estate Investments?
Interest rates have a powerful impact on real estate investments. They influence borrowing costs, property values, rental yields, and even market liquidity. Understanding these effects can help investors make smarter decisions and maximize returns.
Let’s break down the key ways interest rates shape the real estate market.
The Cost of Financing
Interest rates determine how much it costs to borrow money for real estate purchases. Even a small rate change can significantly impact mortgage payments and overall affordability.
- High Interest Rates: When rates rise, loans become more expensive. Monthly mortgage payments increase, reducing how much buyers can afford to borrow. As a result, fewer people enter the market, which slows down housing demand and gives remaining buyers more negotiating power. Sellers may need to lower prices or offer incentives to attract buyers.
- Low Interest Rates: More buyers enter the market when borrowing is cheaper. This increased housing demand may drive up property prices, making investing in real estate more competitive. Investors may benefit from lower mortgage payments, which can improve cash flow and potentially support long-term return objectives. However, returns are not guaranteed and depend on multiple factors.
For real estate investors, financing costs play a major role in profitability. Those who secure low-interest loans may reduce their financing expenses, which can enhance their potential return on investment (ROI), though outcomes are subject to market and property-specific factors.
Property Values
Interest rates and property prices may exhibit an inverse relationship, though this can vary based on local market conditions and broader economic factors. When rates go up, home prices tend to level off or decline. When rates drop, property values typically increase in value.
- Rising Interest Rates: Higher borrowing costs shrink the pool of potential buyers. With less competition, home prices may stabilize or even decrease. This can create opportunities for investors to buy commercial properties at lower prices before the market rebounds.
- Falling Interest Rates: When borrowing is more affordable, demand for homes increases. More buyers in the market can lead to rising property prices. Investors who already own properties benefit from this appreciation and can sell for a higher profit.
Understanding market trends is important. While some investors aim to purchase during lower-price periods and sell during favorable market conditions, real estate values are subject to change and can fluctuate based on broader economic factors.
Rental Yields & Demand
Interest rates also influence the rental market, affecting both supply and demand for rental properties.
- High Interest Rates: When borrowing becomes expensive, fewer people purchase a home, and more turn to renting. This increases demand for rental properties, allowing landlords to charge higher rents. In turn, rental yields improve, making income-producing real estate more attractive.
- Low Interest Rates: When mortgage rates are low, more renters transition to homeownership. Rental demand decreases, which can put downward pressure on rental prices. However, landlords may benefit from lower financing costs, which means they don’t have to charge as much rent to cover their expenses.
Investors looking for rental income should consider how interest rates influence tenant demand and pricing.
Market Liquidity & Investment Timing
The speed at which properties sell—and how easy it is to enter or exit the market—depends heavily on interest rates.
- Low Interest Rates: When financing is affordable, properties sell quickly because more buyers are competing. Investors who flip homes benefit from strong demand and faster transactions.
- High Interest Rates: Homes take longer to sell as buyers are more cautious. Sellers may need to lower prices or offer creative financing options to attract buyers. Long-term investors, however, can benefit from strong rental demand during these periods.
For investors, knowing when to buy or sell based on interest rate trends can make a big difference in profits.
How to Navigate a High-Interest Rate Market
Interest rates play a significant role in shaping real estate investment decisions. When rates rise, borrowing costs increase, impacting purchasing power, property values, and cash flow. However, strategic planning and adaptability can help investors thrive in a high-interest-rate environment. Here’s how:
Monitor Interest Rate Trends
Staying informed about interest rate trends helps investors make proactive decisions. Consider:
- Tracking Economic Indicators: Watch for inflation rates, employment data, and GDP growth, which influence interest rate changes.
- Following Central Bank Announcements: Institutions like the Federal Reserve or the Bank of Canada provide insights into future rate adjustments.
- Understanding Market Sentiment: Stay updated on industry trends and expert forecasts to anticipate potential shifts.
By staying ahead of rate movements, investors can time their investments wisely and make well-informed financing decisions.
Consider Fixed-Rate Mortgages
When interest rates are rising, securing a fixed-rate mortgage can provide long-term financial stability. A fixed-rate loan locks in current rates, protecting against future increases and ensuring predictable monthly payments. Benefits include:
- Predictable payments – Fixed-rate loans offer predictable payment structures, preventing unexpected cost spikes.
- Shielding against future rate hikes – Investors can avoid the risk of rising variable rates, which can erode cash flow.
- Long-term financial planning – Predictable financing costs allow for more accurate budget and investment planning.
If already holding variable-rate loans, investors may explore refinancing options to switch to a fixed-rate loan while rates remain manageable.
Diversify Across Property Types
Spreading investments across different asset types and financing structures can reduce risk in a high-rate environment. Real-estate investment strategies include:
- Mixing property types – Investing in residential, commercial, and multi-family properties can balance risk exposure.
- Exploring cash-flow-positive properties – Prioritize properties with properties with the potential to generate income under varying rate conditions.
- Investing in different markets – Consider areas with growing rental demand, strong job markets, and limited housing supply to minimize market downturn risks.
Diversification ensures that losses in one segment do not significantly impact the overall portfolio.
Evaluate Market Conditions Before Investing
Interest rates don’t operate in isolation—they interact with broader market dynamics. Before making investment decisions:
- Assess Supply and Demand Trends: Understand how rising rates affect buyer demand and rental occupancy.
- Analyze Local Economic Indicators: Job growth, population trends, and industry development influence property values.
- Study Competitor Pricing: Evaluate comparable property prices and rental rates to determine competitive positioning.
A thorough market analysis ensures that investments align with current and future economic conditions.
Plan for Contingencies and Stress-Test Investments
Interest rates impact cash flow, so it’s essential to prepare for worst-case scenarios. Steps to mitigate risk include:
- Running Stress Tests – Analyze how increased interest rates affect loan payments, cash flow, and profitability.
- Building Financial Reserves – Maintain an emergency fund to cover unexpected costs or temporary vacancies.
- Exploring Refinancing Opportunities – If interest rates stabilize or decrease in the future, refinancing can help reduce costs.
By proactively planning, investors can safeguard their portfolios and maintain financial stability.
Take Control of Your Investments
Interest rate fluctuations don’t have to derail your real estate goals. With the right planning, risk management, and financing strategies, you can identify opportunities even in a challenging market.
If you’re looking for tailored advice on how to navigate the market, reach out today—we’re here to help you make informed investment decisions.

How long are you invested in a DST?
Watch this video to understand typical investment timelines for DSTs and find out if they align with your financial goals.

The Benefits of working with the Principals of the Broker Dealer
Learn how working directly with experienced Broker Dealer Principals can enhance your investment journey.

What is it like to own a DST?
Curious about DST ownership? This video breaks down what it's like to invest in a DST and the hands-off benefits it offers.

What kinds of properties qualify for a DST?
Explore the range of properties that qualify for DSTs, from commercial buildings to multifamily units.
Stax helped me shift to passive income and defer my taxes.
Stax guided Ramesh through a successful 1031 exchange and DST investments, allowing him to defer taxes and enjoy hassle-free income.
-Ramesh

Stax made my transition to passive income smooth and stress-free.
Stax helped Shikha complete a 1031 exchange into DSTs, freeing her from property management and allowing her to focus on personal time.
-Shikha

Stax made it easy to switch to passive investments for our retirement.
Stax introduced Sima and Roman to DSTs, allowing them to shift from active property management to a hands-off strategy while maintaining a steady income.
-Sima and Roman
DST Case Stories
Explore testimonials from investors who have collaborated with us. Discover their success stories with 1031 exchanges into Delaware Statutory Trusts (DSTs) and understand how our professional guidance has positively impacted their investment experiences.
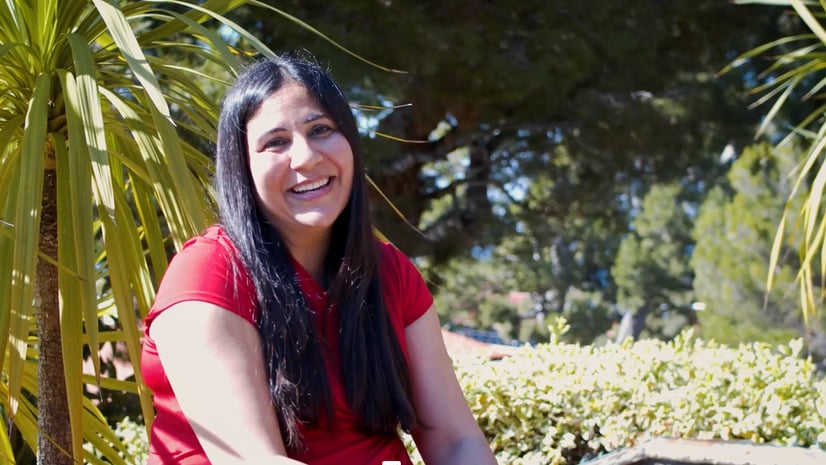

Stax made my transition to passive income smooth and stress-free.
Stax helped Shikha complete a 1031 exchange into DSTs, freeing her from property management and allowing her to focus on personal time.
-Shikha
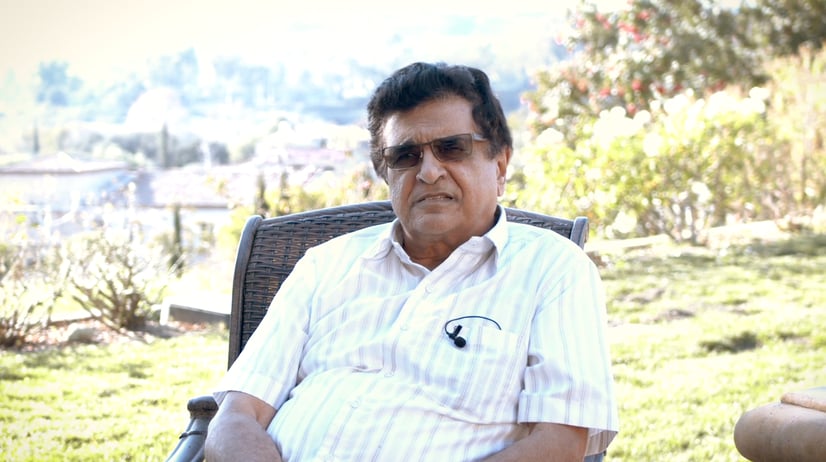

Stax helped me shift to passive income and defer my taxes.
Stax guided Ramesh through a successful 1031 exchange and DST investments, allowing him to defer taxes and enjoy hassle-free income.
-Ramesh
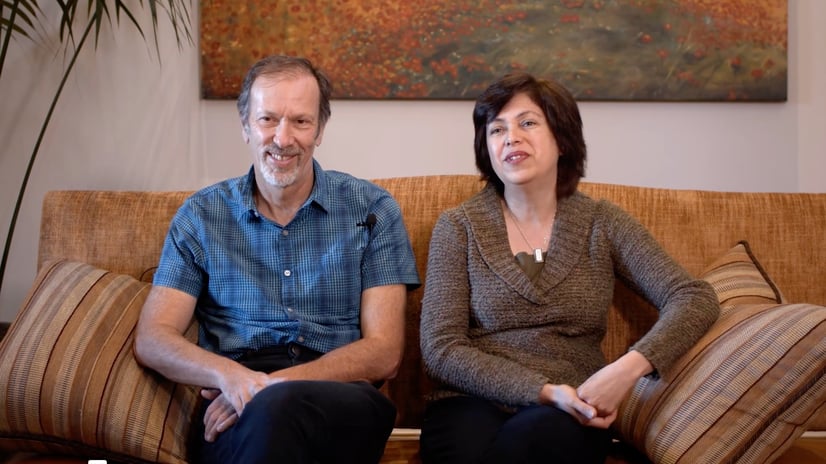

Stax made it easy to switch to passive investments for our retirement.
Stax introduced Sima and Roman to DSTs, allowing them to shift from active property management to a hands-off strategy while maintaining a steady income.
-Sima and Roman
Disclosure
The experiences shared by clients of Stax Capital were given voluntarily without any compensation. These testimonials reflect individual opinions and are not intended as investment advice or guarantees of future results. Each investor should consider their own financial goals, risk comfort, and overall situation before making any investment choices.
Connect
With Us
Your goals matter to us. Fill out the form or call us. Our team will respond quickly with expert advice and customized solutions that meet your investment needs.
Investor Profile
